Home

What is Ganglion Cyst? Causes, Treatment & Symptoms
In this Article

Pregnancy
What is Ganglion Cyst? Causes, Treatment & Symptoms
Updated on 3 November 2023
New mothers, athletes, and individuals with arthritis are prone to swellings on their wrists, hands, knees, ankles and feet, termed a Ganglion cyst. This article discusses a Ganglion cyst, its symptoms, causes, and treatment.
What is a Ganglion cyst?
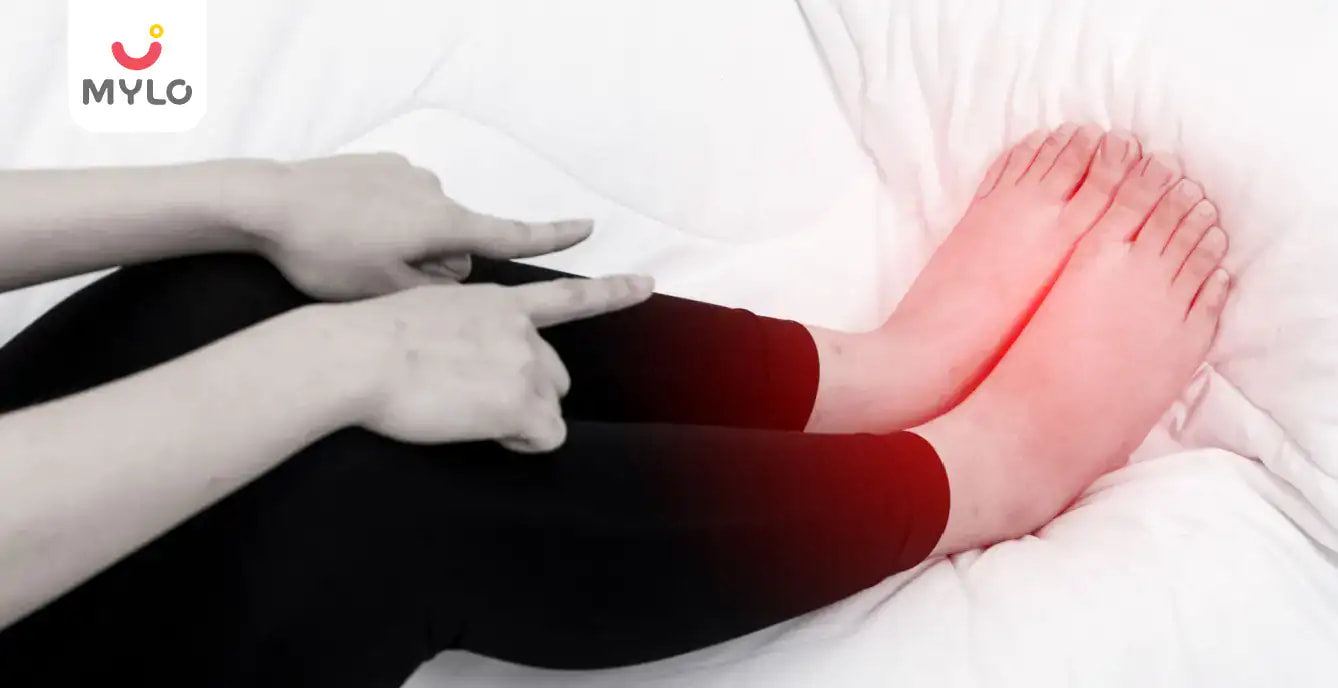
A Ganglion cyst is a swelling or a fluid-filled lump of soft tissue appearing over or around certain body parts. Common locations for a Ganglion cyst include the wrist, Ganglion Cyst on the Finger, foot, knee, and ankle. Out of these, Wrist Ganglion Cyst is the most common among new mothers.
The size, appearance, and shape of a Ganglion cyst may vary according to the location and chronicity of the condition.
What are the causes of a Ganglion cyst?
Ganglion Cyst Causes do not include a definite pathology or a mechanism. Common reasons include:
-
Overuse of a body part during daily activities
-
Repetitive strain
-
Trauma or injury
-
Irritation or friction due to contact with a hard surface
-
Osteoarthritis
Symptoms of Ganglion cyst
Ganglion Cyst symptoms may vary according to where the cyst is present in the body.
Common symptoms include:
-
Pain and discomfort
-
Tingling sensation
-
Difficulty or, in some cases, inability to do daily activities
-
Tingling numbness may be experienced the Ganglion Cyst is near or on a nerve
How does a doctor diagnose a Ganglion cyst?
Diagnosis of a Ganglion cyst is based on a thorough history of the onset of symptoms and daily activities done by the individual. This will reveal a possible cause of developing swelling and pain in the affected area.
The doctor will order tests to confirm the diagnosis, such as:
-
X-ray
-
MRI
-
Ultrasound imaging
-
Analysis of fluid within the cyst
Ganglion cyst treatment
A Ganglion cyst resolves within time but may require treatment for symptoms like pain and swelling. Some of the treatment measures include:
1. Ganglion Cyst Aspiration
The doctor will drain the fluid from the cyst with a needle and syringe. The procedure is mild to moderately painful. Pain relieving medicines will be prescribed after the procedure.
2. Surgical removal of the cyst
In some cases, the cyst may not be visible on examination but is confirmed on investigations.
3. Pain management
Medicines are prescribed to reduce pain and swelling in a non-surgical treatment protocol.
4. Precautions and other measures
The affected part should rest through minimal activity, supportive braces and icing. It is also advisable to wear comforting shoes for a Ganglion Cyst on Foot and ankle. Wrist and knee braces are available for Ganglion Cyst of Knee and Wrist Ganglion Cyst.
Other treatments may include Ganglion Cyst Ayurvedic Treatment, Physiotherapy, and Ganglion Cyst Home Treatment. However, It is advisable to consult a doctor before deciding on any treatment.
How to prevent a Ganglion cyst?
Preventive measures for a Ganglion cyst are as follows:
-
Avoid repetitive movements at a particular joint.
-
Take frequent breaks to avoid muscle and joint strain.
-
New mothers must adopt ergonomic modifications like using supports and cribs to handle their children.
-
Avoid repetitive contact with hard surfaces that may lead to friction injuries
Conclusion
A Ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled round sac that develops on the wrist, foot, ankle, fingers, and knee. It generally occurs due to repetitive strain on muscles and joints in new mothers, athletes, and individuals with arthritis. It usually resolves by itself but may sometimes require medical or surgical treatment.
FAQs
-
Is Ganglion Cyst painful?
A Ganglion cyst may be asymptomatic in some individuals but some may experience intense pain, swelling, discomfort and difficulty in daily activities.
-
Is Ganglion Cyst dangerous?
A Ganglion cyst by itself is not dangerous unless it is present on a nerve or be the initial signs of a tumor beneath.
-
Can a Ganglion cyst spread to other body parts?
A Ganglion Cyst is benign, meaning it is localised and does not spread to other body parts.
-
Can I do exercise for the wrist Ganglion Cyst?
Exercise is not advisable for wrist Ganglion Cyst or any other cyst. Repetitive movements should be avoided and it should be allowed to heal with adequate precautions.
-
Which doctor is best for a Ganglion cyst?
An orthopedic doctor is qualified to deal with any type of Ganglion cyst.
References
- Gregush RE, Habusta SF. (2022). Ganglion Cyst. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Minotti, P, Taras, J.S. (2002). Ganglion cysts of the wrist. www.jhandsurg.org



Written by
Roohi Kalra
Get baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Questions
Hello frnds..still no pain...doctor said head fix nhi hua hai..bt vagina me pain hai aur back pain bhi... anyone having same issues??

Kon kon c chije aisi hai jo pregnancy mei gas acidity jalan karti hain... Koi btayega plz bcz mujhe aksar khane ke baad hi samagh aata hai ki is chij se gas acidity jalan ho gyi hai. Please share your knowledge

I am 13 week pregnancy. Anyone having Storione-xt tablet. It better to have morning or night ???

Hlo to be moms....i hv a query...in my 9.5 wk i feel body joint pain like in ankle, knee, wrist, shoulder, toes....pain intensity is high...i cnt sleep....what should i do pls help....cn i cosult my doc.

Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |